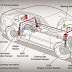
ELECTRONIC STABILITY PROGRAM (ESP) is the active safety
feature in the vehicle that is used in many modern vehicles as a Mechatronic
control system. This feature comes into play when the car goes through
under-steer, over-steer, or split mu etc. ESP helps in improving, the cornering
and control over vehicle by monitoring slip at the wheels. ESP senses the
actual direction of vehicle motion and desired direction of motion (by steering
wheels direction).
Types of sensors used
- Wheel angular speed sensor
- Steering angle sensor
- Yaw rate sensor
- Accelerometer (Lateral accelerator sensor i.e centripetal acceleration)
- Suspension pressure sensor
Working of ESP
 When the vehicle
senses a loss of traction or a slip, braking is automatically applied to all 4
wheels individually and engine power is reduced to help secure the safety of
the vehicle. When there is instability in the vehicle, sensors sense it and
send that information to the ESP controller. For example, if the steering wheel
refuses to turn due to over-speed turning (under-steering), the vehicle will
take control to steer toward the inner curve i.e. brakes are applied to inner wheels to create the yaw moment in the vehicle.
Also, when the vehicle begins to spin from abrupt steering handling
(over-steering), the vehicle will take control to steer toward the outer curve
i.e. brakes are applied to outer wheels to create the compensation moment (to
balance the undesired yaw angle) by the help of friction ( shown in figures).
When the vehicle
senses a loss of traction or a slip, braking is automatically applied to all 4
wheels individually and engine power is reduced to help secure the safety of
the vehicle. When there is instability in the vehicle, sensors sense it and
send that information to the ESP controller. For example, if the steering wheel
refuses to turn due to over-speed turning (under-steering), the vehicle will
take control to steer toward the inner curve i.e. brakes are applied to inner wheels to create the yaw moment in the vehicle.
Also, when the vehicle begins to spin from abrupt steering handling
(over-steering), the vehicle will take control to steer toward the outer curve
i.e. brakes are applied to outer wheels to create the compensation moment (to
balance the undesired yaw angle) by the help of friction ( shown in figures).
TO BE CONTINUED...