Clutch
Bridges the gap between zero revolution wheel and non zero
revolution of IC engine
Its a mechanical devices
that transmits power produced by the engine to the gear box by the
frictional resistance of the rough surfaces of the flywheel and clutch lining(clutch
plate).
The gear transmission is not possible at high rpm, it may create lot of noise and may cause failure in gears
due to sudden impacts. Hence the clutch was introduced that can engage and
disengage the transmission from engine
Main types of clutches
- Dry clutch-Used in normal power engine vehicles it has no liquid fluid surrounded other than air
- Wet clutch-This type of clutches are used for very high power engine vehicles as its immersed in a cooling lubricant that keeps surfaces clean and provides smoother performance and longer life
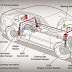
Main components of the clutch system
Working of the clutch
The Flywheel is connected to crankshaft of engine and the transmission
is connected to clutch plate both having rough surfaces. When the clutch plate is in touch with
flywheel the torque is transmitting towards transmission by the action of
friction this is called engagement of clutch
The pressure plate is bolted with the flywheel and at the
center of diaphragm spring there is a special kind of bearing called throw-out
bearing. The clutch disc is in between flywheel and pressure plate and shaft
from clutch disc passes through throw-out or thrust bearing. This type of bearing slides
on shaft towards the clutch disc and lifts the clutch plate from flywheel
whenever the clutch pedal is pushed this is called clutch disengagement.The springs in the clutch plate absorb the sudden impact
during the engagement
Double clutch transmission DCT
Modern technology of clutch
It has two clutch plates connected to two transmission shafts
one for even gear and one for odd gears. when the vehicle is accelerating in
one gear the other gear is already ready for acceleration. This gives the
vehicle continues acceleration without the interference of gear shifting













0 comments:
Post a Comment